Retrospective Analysis on GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS)

Introduction
Integrating security into a widely used platform like GitHub is both a challenge and an opportunity to enhance its resilience. Securing applications at the development stage is now considered essential, ensuring that security becomes a proactive process rather than a reactive one.
This article explores GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS), a suite of tools designed to help developers and organizations identify vulnerabilities, manage dependencies, scan for secrets, and enforce best practices—all without requiring manual intervention in every workflow. But does GHAS truly live up to its promise?
What is GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS)
GHAS is a free feature on public repositories, it is also an add-on for GitHub Enterprise Cloud (GHEC) and GitHub Enterprise Server (GHES), providing developers and security professionals, with a powerful security toolkit. It gets integrated seamlessly offering features like:
- Code scanning: detects security vulnerabilities in your source code using CodeQL.
- Secret scanning: identifies and prevents hardcoded secrets from being exposed or pushed in commits.
- Dependabot: raises alerts and keeps dependencies secure and up to date.
- Dependency Graph: is a feature in GitHub that maps out all the dependencies of a repository. Dependabot utilizes this information to monitor for any security vulnerabilities within these dependencies.
- Security Overview: a dashboard providing visibility into security risks across repositories.
- Security Policies (SECURITY.md): defines security protocols and guidelines for vulnerability management.
1. GHAS in public vs private repositories
GitHub already offers many security features for free; especially for public repositories. But GHAS supercharges your security with advanced capabilities when you have a private organization The table below represents the different functionalities between public and private repositories with or without a GHAS license.
| Feature | Public Repositories | Private Repositories (without GHAS License) | Private Repositories (with GHAS license) |
| Dependency Graph | Enabled | Enabled | Enabled |
| Dependabot Alerts | Enabled | Enabled | Enabled |
| Dependabot Security Updates | Enabled | Enabled | Enabled |
| Code Scanning | Enabled | Not Available | Enabled |
| Secret Scanning | Enabled | Not Available | Enabled |
| Security Overview | Enabled | Not Available | Enabled |
| Security Policies (SECURITY.md) | Enabled | Not Available | Enabled |
2. New Licensing Model: Unbundled GHAS
GitHub has recently announced that, starting April 1, 2025, GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) will be unbundled into two standalone products:
- GitHub Secret Protection: This product focuses on detecting and preventing secret leaks before they occur. It includes features such as push protection, secret scanning, AI-powered detection with a low false positive rate, and security insights. This GitHub Secret Protection will be available at a cost of $19 per month per active committer.
- GitHub Code Security: This offering aims to help developers identify and remediate vulnerabilities more efficiently. It encompasses features like code scanning, Copilot Autofix, security campaigns, Dependency Review Action, and more. GitHub Code Security will be priced at $30 per month per active committer.
GitHub Team plan that customers will be able to purchase these products without requiring a GitHub Enterprise subscription, making advanced security features more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
For more detailed information, you can access to GitHub’s official announcement via the link I provided at the end of this article.
3. GHAS Features Breakdown
Security Overview
Security Overview is a control center for viewing and managing security risks across repositories. It provides:
- A centralized dashboard to track vulnerabilities in all repositories
- Stats and insights into unresolved security alerts
- The ability to enforce security policies organization-wide

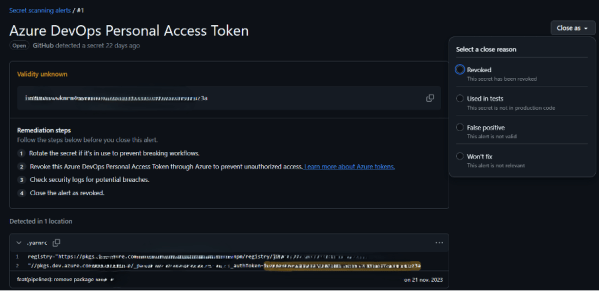
Secret Scanning
Secret Scanning is one of the critical features of GHAS, designed to prevent accidental exposure of sensitive information such as API keys, passwords, and tokens. It continuously scans repositories for known secret patterns and alerts, via mail and notifications, when a secret is detected.
Key Benefits:
- Proactive Leak Prevention: detects secrets in real-time before they are pushed to production. And one of the most proactive features in Secret Scanning is the ability to block a push when a high-confidence secret is detected.

- Integration with Cloud Providers: Alerts cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) when their credentials, with a certain regex pattern, are detected. Allowing them to revoke and replace compromised keys.
- Comprehensive Historical Scanning: can scan an entire repository’s history to detect secrets that were committed in the past.
Managing Secret Scanning Alerts:
When a secret is detected, GitHub provides options to manage alerts effectively:
- False positive: if the detected string is not actually a secret
- Used in tests: an intentionally committed secret (example: test token), this way developers can dismiss the alert with a justification.
- Revoked: once the exposed secret has been properly rotated and removed, the alert can be marked as resolved.
- Won’t fix: when the alert is irrelevant
Code Scanning
Code Scanning is the most crucial feature of GHAS that helps detecting and fixing security vulnerabilities in the source code before it reaches production. It utilizes CodeQL, GitHub’s query-based analysis engine, to scan code for known security issues and best practice violations.
Key Benefits:
- Early Detection of Security Issues: identifies vulnerabilities before they become critical problems. It gives enough details about the detected issues so you can handle them.
- Customizable Analysis and seamless integration with GitHub Actions: developers can either run a default CodeQL workflow or write down a custom CodeQL queries to detect organization-specific security issues (check the yaml file exemple below)
- Supports Multiple Programming Languages: like JavaScript, Python, C, Java, C++, Go,…
Managing Code Scanning Alerts:
- Reviewing Alerts: each detected vulnerability is presented as an alert with severity ratings and suggested fixes. The alert appears not only in the security board but also in the Pull Request tab.
- Fixing Issues Proactively: Suggested fixes additionally to auto-fixes using Copilot, help developers resolve vulnerabilities quickly before merging PRs.
- Dismissing False Positives or Tests: developers can dismiss alerts that are not applicable or just used for tests, providing justification for the action.

Example of a CodeQL.yml file for an Angular Application
name: CodeQL.yml
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
analyze:
name: CodeQL Analysis
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
actions: read
contents: read
security-events: write
steps:
– name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
– name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: ‘lts/*’
– name: Initialize CodeQL
uses: github/codeql-action/init@v3
with:
languages: javascript-typescript
build-mode: auto
– name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v3
with:
category: /language:javascript-typescript

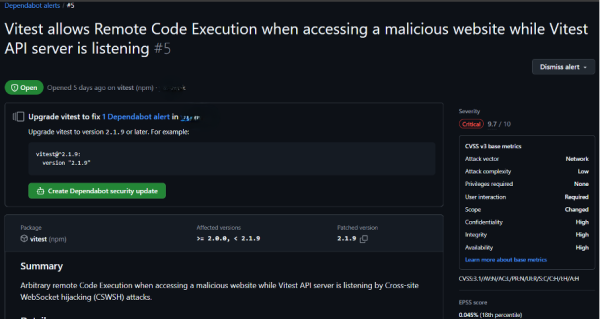
Dependabot
It is GitHub’s built-in tool for monitoring. It automatically scans dependency files and alerts users if a security vulnerability, or an outdated package version, is found.
Key Benefits:
- Automated Vulnerability Detection: scans dependency files for known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries.
- Automatic Pull Requests: Creates pull requests with the necessary security updates.
- Supports Multiple Package Managers: Works with npm, Nuget, Maven, Gradle, Python (pip), and more. You can add their registries in dependabot.yml file.
- Configuration via dependabot.yml: Allows customized and fine-grained control over update frequency and package versioning.
Dependabot.yml:

version: 2
updates:
– package-ecosystem: “nuget”
directory: “/”
schedule:
interval: “weekly”
day: “sunday”
target-branch: “main”
open-pull-requests-limit: 5
labels:
– “dependencies”
– “nuget”
– package-ecosystem: “npm”
directory: “/”
schedule:
interval: “weekly”
day: “sunday”
target-branch: “main”
open-pull-requests-limit: 5
labels:
– “dependencies”
– “npm”
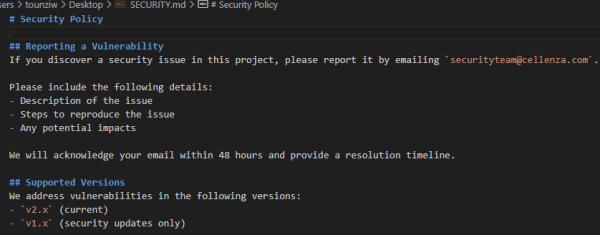
Security Policies
Projects can include a SECURITY.md file to their repository’s root. Its key benefits are to:
- Define how security vulnerabilities should be reported.
- Provide guidelines for handling security issues.
- Outline best security practices for contributors.
- For open-source projects, a well-documented SECURITY.md file enhances transparency and trust.
# Security Policy
## Reporting a Vulnerability
If you discover a security issue in this project, please report it by emailing `securityteam@cellenza.com`.
Please include the following details:
– Description of the issue
– Steps to reproduce the issue
– Any potential impacts
We will acknowledge your email within 48 hours and provide a resolution timeline.
## Supported Versions
We address vulnerabilities in the following versions:
– `v2.x` (current)
– `v1.x` (security updates only)
Honest Review
GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) provides valuable security insights on both GitHub and Azure DevOps when enabled through project settings. But the GitHub integration is more advanced and customizable compared to Azure DevOps, making it a more powerful choice for security management.

While GitHub provides some level of customization, it still has certain limitations:
- Security Overview Restrictions: GHAS lacks a consolidated dashboard for organizations with multiple repositories. Ideally, it would be more effective if every repository had the same Security Overview structure and metrics, instead of minimal and simple dashboard with no stats.
- Limited Permissions Customization: The Contributor role grants users broad security rights and extensive permissions in GHAS, instead of restricting security-related actions only to a dedicated security operating role.
- GitHub Actions Path Ignore Limitations: for CodeQL file filtering task, the “paths-ignore” functionality is not fully effective for certain technical stacks, limiting its ability to selectively exclude files or directories from security scans. To work around this limitation, you will need to use the Filter SARIF action from the GitHub Marketplace.: Filter SARIF · Actions · GitHub Marketplace
Despite these limitations, I see GHAS as a proactive security team integrated directly into GitHub, continuously scanning code, dependencies, and secrets to mitigate security risks before they escalate. Also, this unbundling plan allows organizations greater flexibility to adopt the specific security features they need without committing to the entire GHAS suite.
Reference for unbundled announcement: Evolving GitHub Advanced Security: Greater flexibility, easier to access – GitHub Resources
Reference for GHAS features overview: GitHub security features – GitHub Docs